INTRODUCTION
ESCAPE-2 develops world-class, extreme-scale computing capabilities for European operational numerical weather and climate prediction, and provide the key components for representative benchmarks to be deployed on extreme-scale demonstrators and beyond. It continues the pioneering work of the ESCAPE project.
Learn moreSTRUCTURE
The project activities are organised around four technical and two cross-cutting work packages. ESCAPE-2 training will focus on filling the gap between science and hardware specific code levels by employing the newly developed DSL toolchain to key algorithmic motives and applying it to achieve performance portability of novel mathematical concepts as developed in ESCAPE-2.
Learn moreCONSORTIUM
The ESCAPE-2 consortium covers the scientific and technical expertise along the value chain of novel accelerator hardware, programming environment, weather and climate application software, and energy efficiency diagnostics. The consortium represents world-leading European global and key regional weather centres translating the benefits of ESCAPE-2 into substantial societal benefit.
Learn moreValue proposition
Partners
Reports
HPCW Benchmark Versions
Prototypes
OUR RESULTS
ESCAPE-2 paves the way for the European weather and climate prediction community towards the exascale.
Escape-2 connects the dots. Developing bespoke and novel mathematical and algorithmic concepts, combining them with proven methods. Providing exascale-ready production benchmarks to be operated on extreme-scale demonstrators. ESCAPE-2 also combines cross-disciplinary uncertainty quantification tools (URANIE) for high-performance computing, originating from the energy sector, with ensemble based weather and climate models to quantify the effect of model and data related uncertainties on forecasting. Read all about it in our reports.
Read more
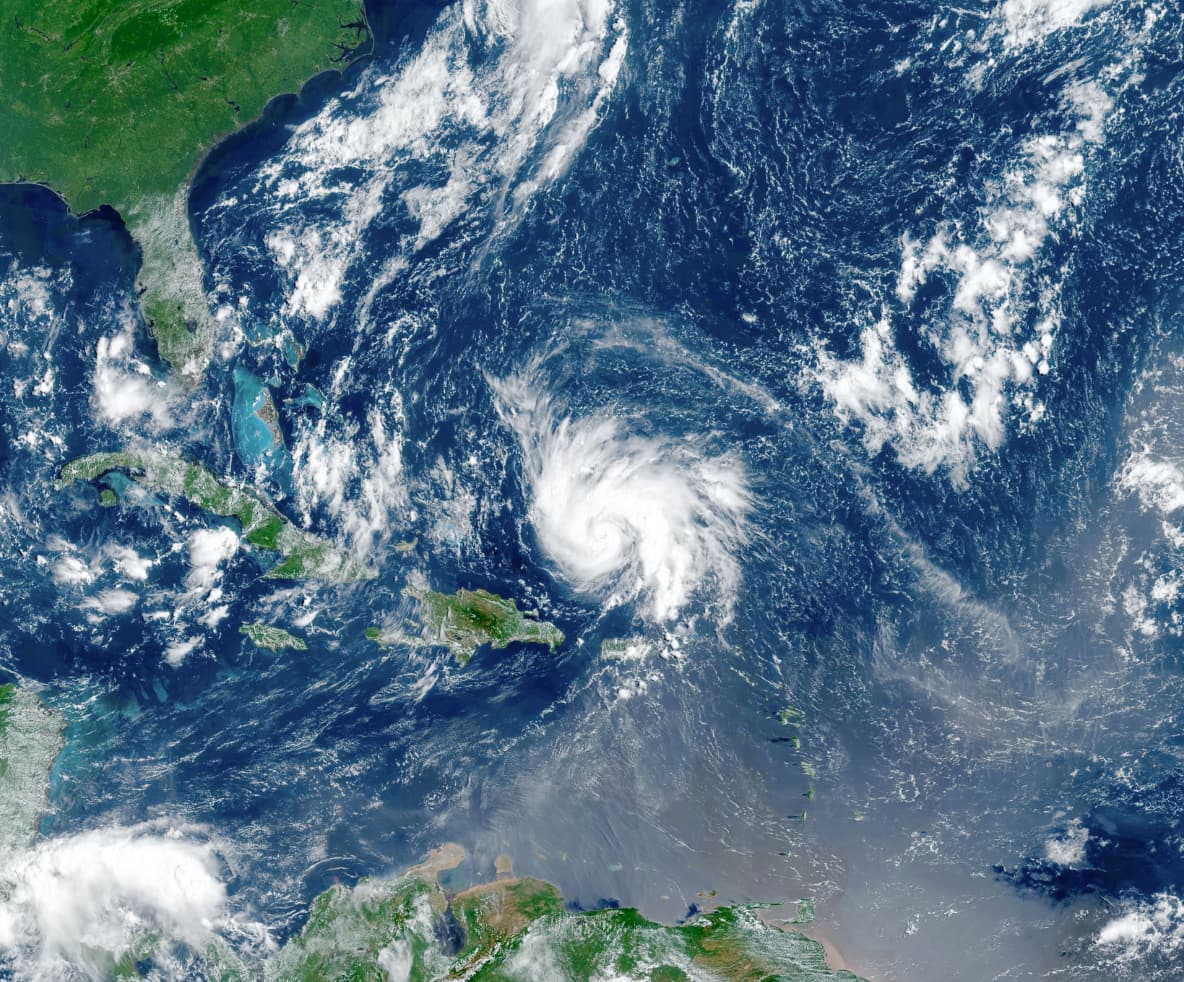
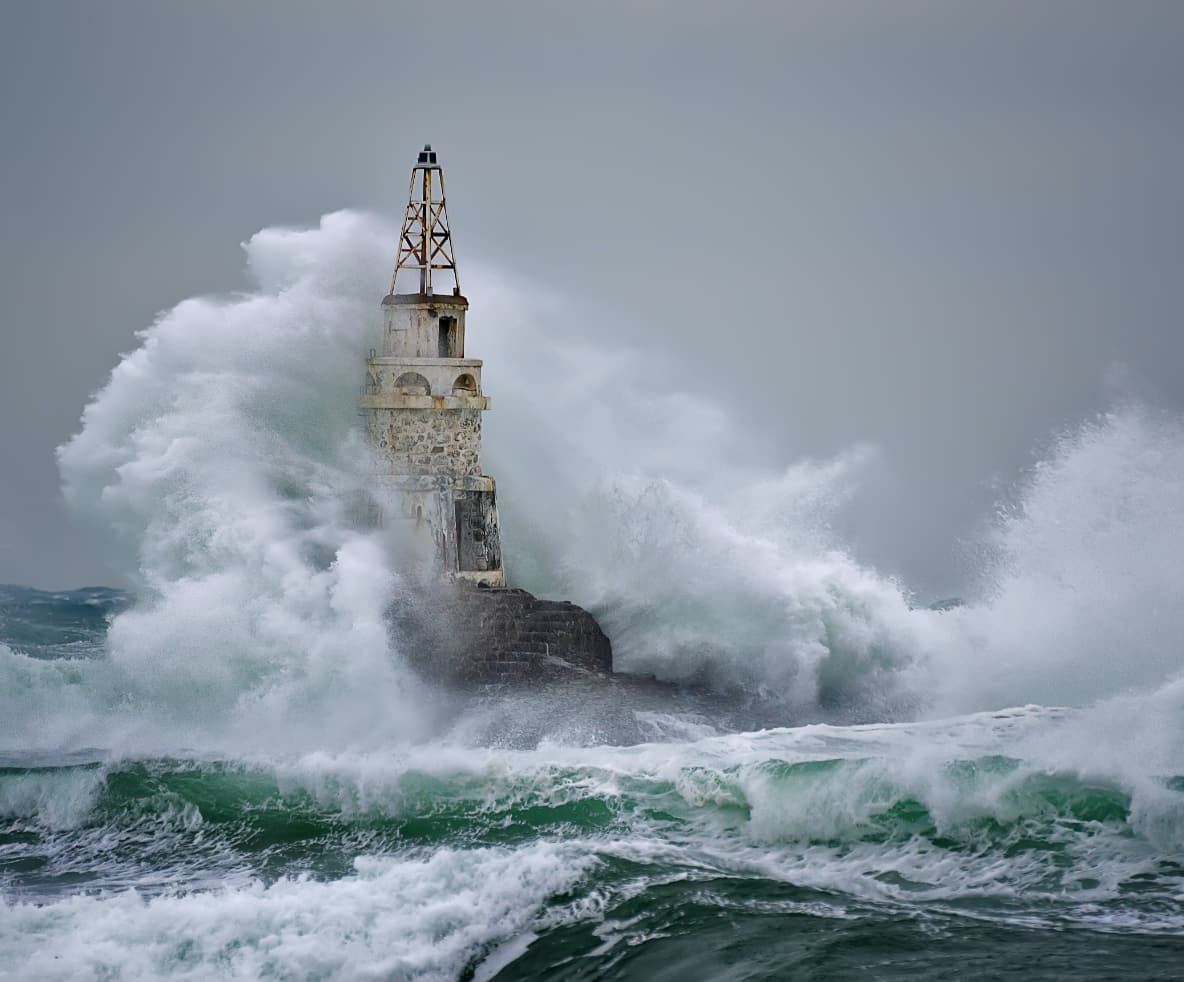


IMPACT
ESCAPE-2 employs exascale high-performance computing for high-resolution weather and climate forecasting.
Weather- and climate-related disasters have caused $2.4 trillion in economic losses and nearly 2 million deaths globally since 1971 as a result of hazards such as droughts, extreme temperatures, floods, tropical cyclones and related health epidemics, according to a report by WMO. Notably, the United Nation’s Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction concluded that direct and indirect losses from natural hazards of all kinds have even been underestimated by at least 50%. More precise forecasts and their uncertainty bounds in both time and space are critical for human activities and concerns such as travel, health, work, and safety. While there is no control about the weather itself, its impact on society through forecasting and preparation has been drastically reduced, with advances in predictive skill enabling more timely decisions.
Read more
WOMEN IN SCIENCE
ESCAPE-2 contributes to gender balance in computer science, numerical technologies and geophysical sciences for weather and climate.
The ESCAPE-2 project incorporates aspects of subject areas such as computer science, numerical technologies in science and engineering, and geophysical sciences related to weather and climate. These subjects belong to disciplines in which women are significantly under-represented. Indeed, the low percentage of female participants in the project illustrates a typical gender imbalance in many skilled workforces active in these subject areas. However, the long term and multi-national application of ESCAPE-2’s outcomes, related training, and wide-ranging dissemination to young scientists and the general public makes ESCAPE-2 a valuable vehicle for promoting gender equality and raising awareness of career opportunities in these disciplines.
Read more

OUTREACH
Prompting a paradigm shift in the understanding and use of Domain Specific Languages impacting weather and climate model design and use.
To achieve this paragdigm shift, ESCAPE-2 provides training and actively shares its results, promoting the use of weather and climate dwarfs and the application of the HPCW benchmark in co-design, model development, as well as in training and education.
Read more